Video demo:
Description:
The user is at the center of attention in every interactive application. This is particularly true for the random walker segmentation approach. The user draws labels directly on the image, which makes such approach highly intuitive. In counterpart, this type of interaction requires a fast visual response in order to be effective. However, for random walker segmentation, the computation time depends on the size of the image, and large image segmentation can suffer from serious lags (that can reach several seconds for a 1500x1500 image).
FastDRaW (for Fast Delineation by Random Walker) is an interactive graph-based segmentation approach that uses a coarse-to-fine strategy combined with a focused region of interest (ROI) to drastically reduce the computation time of the random walker segmentation. First, the random walker segmentation approach is performed on a down-sampled version of the image inside the ROI. Then, a second random walker segmentation is performed on the full resolution image (Fig. 1). FastDRaW is highly responsive rendering the segmentation interactive for large images.
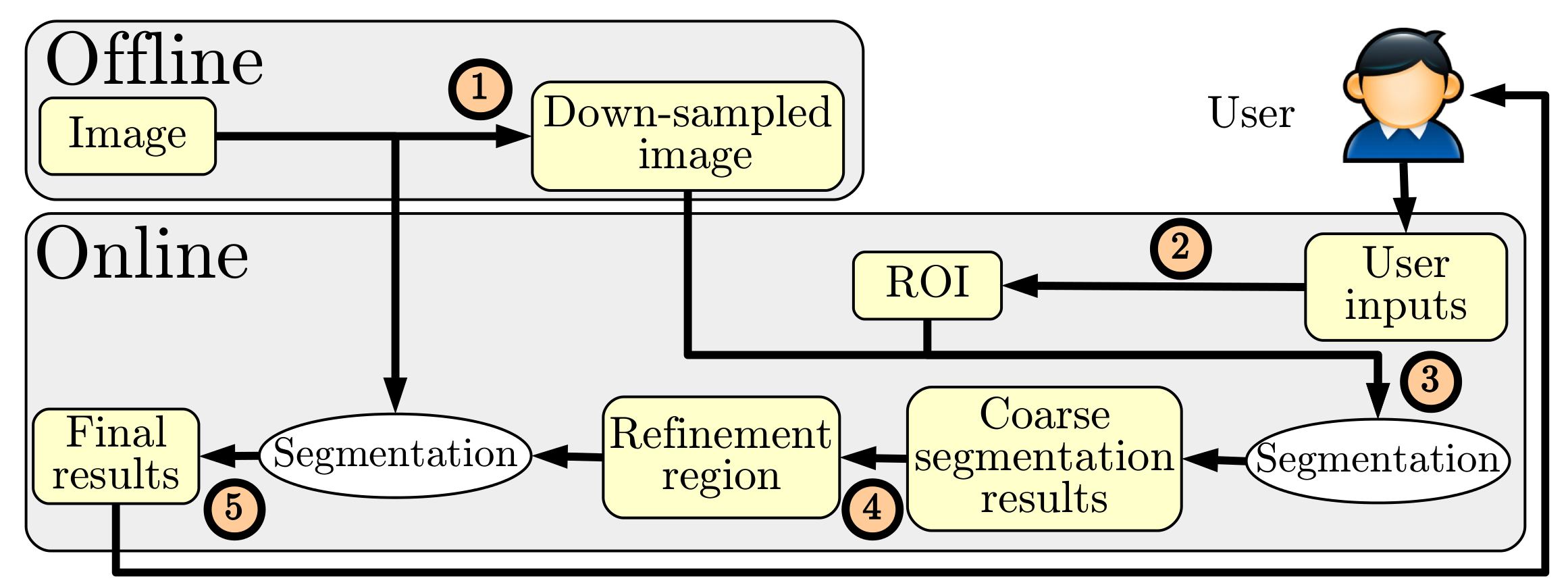
From the user’s perspective, the FastDRaW interaction is identical to the random walker segmentation approach, meaning that the inputs correspond to drawing some labels on the image. Starting from these labels, the following processing is hidden to the user (see Fig. 2): (i) first the labels are used to compute a ROI that discards redundant labels, then (ii) a coarse contour is obtained on the down-sampled image, (iii) this contour is used to compute a refinement region and perform a second segmentation on the full resolution image.
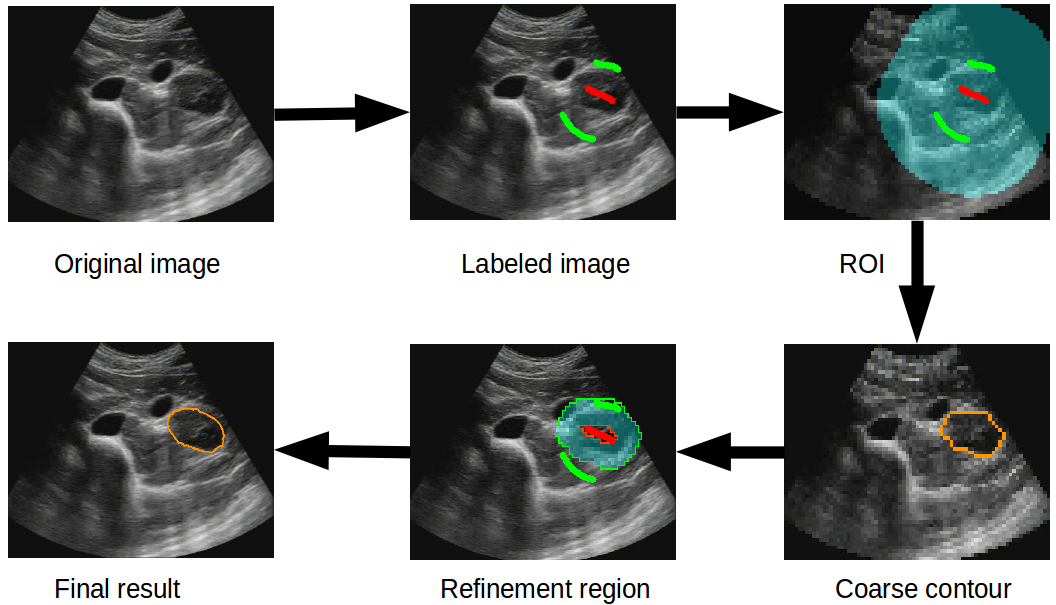
Because the segmentation is only performed in restricted regions (ROI and refinement regions, represented with the blue region in Fig. 2), the computation is very fast. For a standard medical image size of 512x512, the computation time is about 0.13 ± 0.003 s allowing a continuous feedback display during the drawing (in comparison with the random walker, the computation time is 1.23 ± 0.03 s for the same size). For a larger format of 1500x1500 pixels, the computation reached 1.18 ± 0.04 s which is reasonable for such interactive application(in comparison with the random walker, the computation time is 10.18 ± 0.25 s for the same size).
For more details, we refer interested readers to the article, here.
GitHub project:
link to repository
git clone https://github.com/hgueziri/FastDRaW-Segmentation.git
The code is written in Python 2.7 and require scikit-image library. Two examples are provided:
- Example 1: uses matplotlib library to create a simple interactive window to draw labels. The drawings are somewhat slow and no continuous feedback is displayed. The example serves as a comparison between the random walker segmentation algorithm and FastDRaW.
- Example 2: uses OpenCV2 library to create the image window. OpenCV window allows a more advanced interaction and drawing. The example illustrates the continuous feedback display during the drawing.
Python demo:
- for Windows (54 Mb)
- for Linux (154 Mb)
The demo comes with a python virtual environment and all the required libraries (i.e., scikit-image, PyOpenCV, scipy and numpy). However, it may require to install python 2.7.